6 Symptoms of a Blown Alternator Fuse or Fusible Link
A properly functioning alternator is absolutely essential for powering your vehicle’s electrical system and charging your battery. However, if your alternator fuse blows, your charging system will fail. Without alternator power, you’ll quickly find yourself stranded with a dead battery.
The alternator itself may appear to be faulty, but a blown fuse may be the real culprit. Learn the symptoms of a blown alternator fuse or fusible link and where it is located so you can accurately diagnose and troubleshoot this issue.
Symptoms of a blown alternator fuse
When your alternator fuse blows, it can cause a variety of side symptoms, some of which are serious enough to leave the driver stranded on the side of the road. It is essential to be aware of these potential symptoms if you are trying to resolve the issue at hand as quickly and efficiently as possible.
1) Dead Battery
If you start your car and feel a lack of power, it is a good idea to do a quick check of your alternator fuse. A blown fuse will prevent your alternator from charging your vehicle’s battery as intended, draining all of its available voltage/amperage.
2) Strange Electrical Issues
If you suddenly experience one or more strange electrical issues, it’s another sign that there’s a problem with your vehicle’s charging circuit. When your battery starts to lose voltage due to a lack of charge, many vehicle systems can start to react abnormally.
3) Dim the Lights
If your car’s lights appear dim, it could be an indication of a malfunction in the charging system. While many issues could be at play, the presence of a blown alternator fuse or fusible wires shouldn’t be overlooked.
4) Low Charge Light
If your vehicle’s instrument cluster starts to show a “low charge” light, it’s almost certainly due to a problem with your vehicle’s alternator circuit. You should perform a simple continuity check on your vehicle’s alternator fuse.
5) Blown, Broken, or Deformed Fuse or Fusible Wire
In many cases, a quick inspection will physically determine that your alternator’s fusible wire is blown. The wire itself will look deformed, broken, or burnt. However, if you have any doubts, you can use a digital multimeter to check the condition of this fusible wire.
You can confirm a blown fuse by checking for continuity between both ends of this wire. Lack of continuity indicates a mistake.
6) Stalling
In the worst case scenario, a blown alternator fuse can actually kill your vehicle while in use. This happens when the vehicle’s charging system fails and the battery goes into a discharged state. In this case, it’s like someone suddenly turns the key in the affected vehicle to the “off” position.
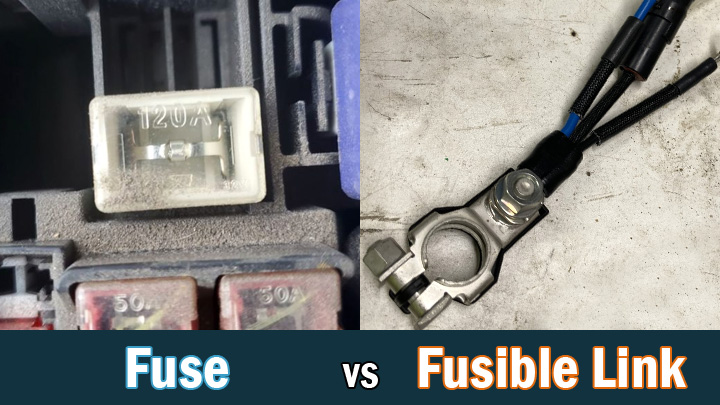
Fuses vs. Fusible Wire
Many well-intentioned drivers confuse general-purpose fuses with fusible wire fuses. When talking about generators or generator circuits, most people who talk about fuses are actually referring to the fuses in the charging system.
The purpose of this particular fuse is to protect many vehicle systems from potentially catastrophic power surges. Without such protection, such surges could melt wires, burn out smart modules, or cause a fire.
Fusible links are designed to melt and disconnect, creating an open condition in a given circuit and preventing further damage to the electrical system. Fusible links are typically made from significantly thinner wire than the wire normally present in the circuit they connect. This effectively creates a weak spot where a controlled wire failure can occur if an overcurrent condition occurs.
A blown fuse must be replaced before power can be successfully restored to a particular circuit.
Where is the alternator fuse located? In most cases, your vehicle’s in-line alternator fuse or fuses are located between the vehicle’s battery positive terminal and the alternator positive cable. Alternatively, in some vehicles, this fuse may be located between the battery positive lead and the main positive terminal in the vehicle’s fuse/junction box.
If your vehicle uses standard fuses, it’s usually located in the fuse box in the engine compartment. Because generators require high-current fuses, this fuse will be larger than the standard blade fuses used for smaller electrical components such as tail lights.
What you need to know about defective starter fuses It’s important to remember that your vehicle’s starter fuse doesn’t just randomly blow for no reason. There must have been a significant voltage spike or an intermittent short to ground for this to happen. For this reason, it is important to diagnose the underlying issue that caused your vehicle’s alternator fuse to blow; not doing so could result in recurring failures.
An internal fault in the alternator and a poor circuit connection can both cause an alternator fuse to blow. In these situations, excessive current draw can cause excessive thermal stress on the affected circuit, potentially causing the in-line fuse to blow.
Jump-starting a dead battery is also a common cause of a blown alternator fuse. In such situations, it is sufficient to simply replace the affected fuse, unless of course such a deteriorating situation occurs again.